Perforated metal, also known as perforated sheet, plate, or screen, is a versatile material with patterns of holes, slots, or decorative shapes achieved through manual or mechanical stamping or punching processes. It is made from diverse materials including stainless steel, cold-rolled steel, galvanized steel, aluminum, and other metals.
Specifications
Hole Patterns
Perforated metal is available in a range of hole patterns, each designed for specific uses and aesthetic preferences:
- Round Hole Pattern: The most common pattern, suitable for a variety of applications. It provides good ventilation and is visually appealing. Typical hole sizes range from 1mm to 100mm.
- Square Hole Pattern: Offers a uniform look and is often used for architectural and protective screens. Standard hole sizes range from 3mm to 75mm.
- Slotted Hole Pattern: Features elongated openings ideal for screening and sorting applications. Common sizes vary from 10mm x 20mm to 20mm x 100mm.
- Hexagonal Hole Pattern: These six-sided holes are used for applications needing efficient passage of air or fluids and are common in decorative applications. Sizes are typically from 6mm upwards.
- Decorative Hole Pattern: Customized to include various artistic and intricate designs suitable for aesthetic purposes in architectural projects. Sizes and shapes are designed to specific requirements.
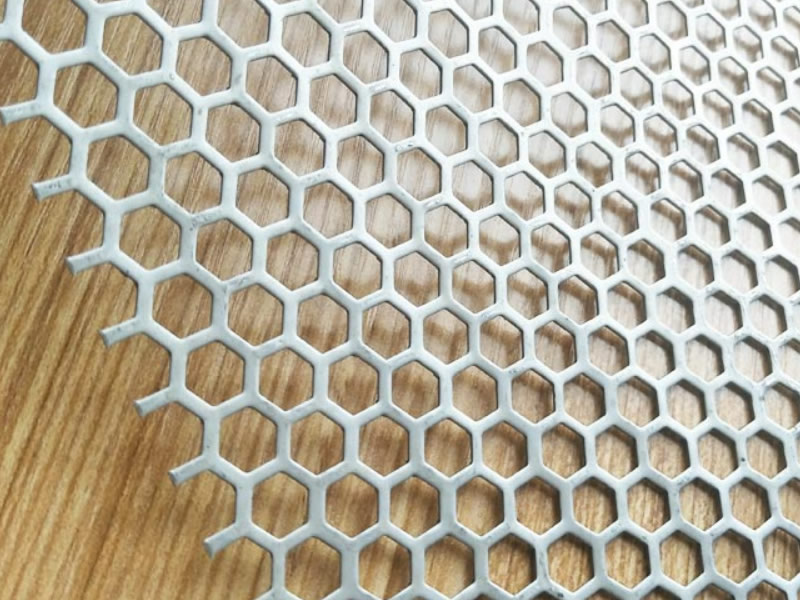
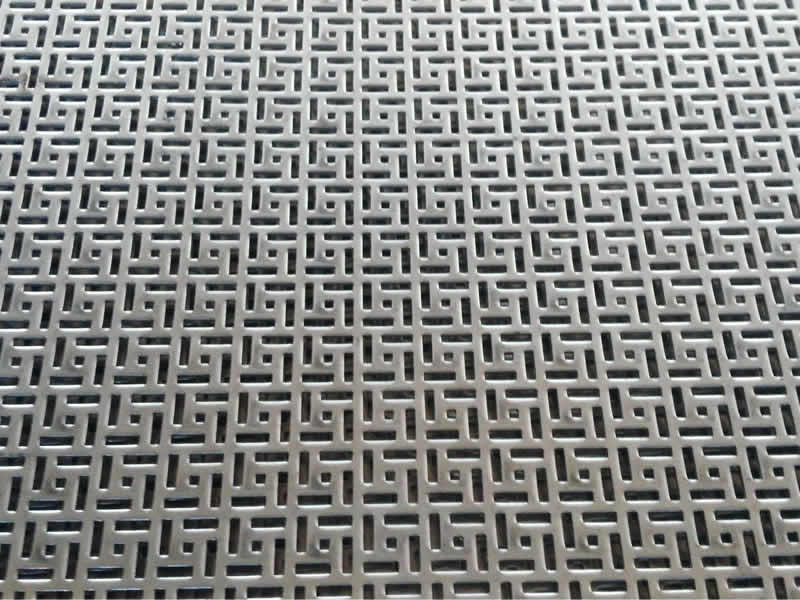
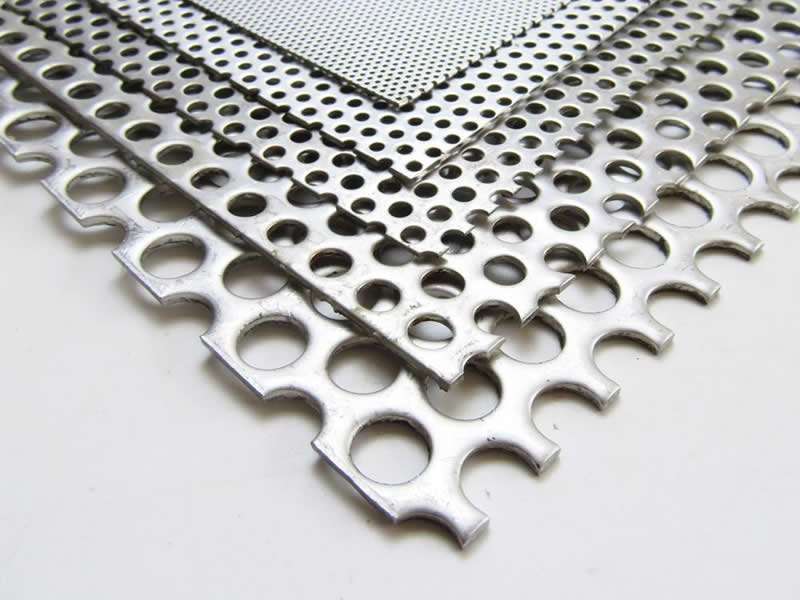
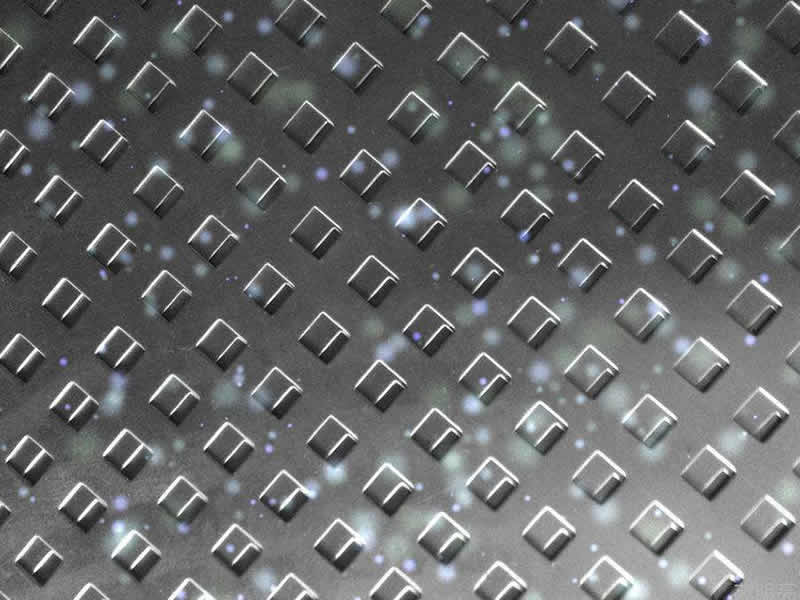
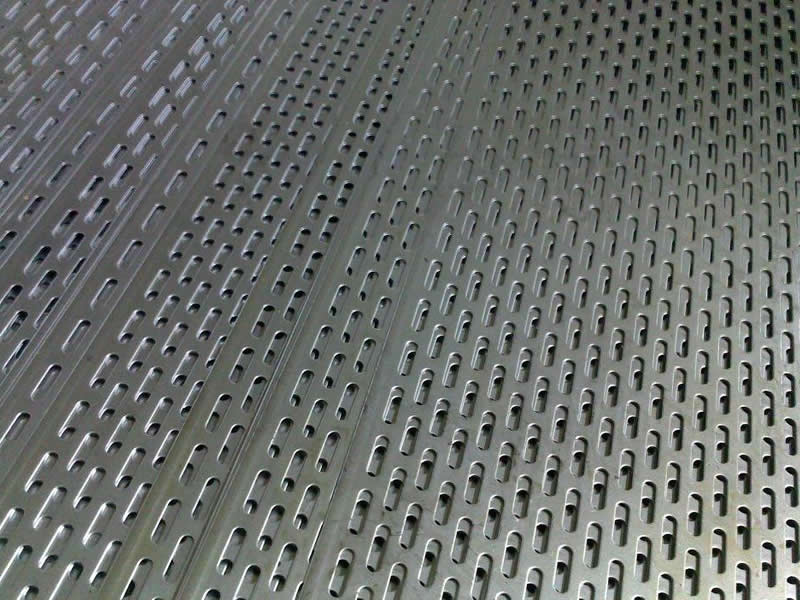


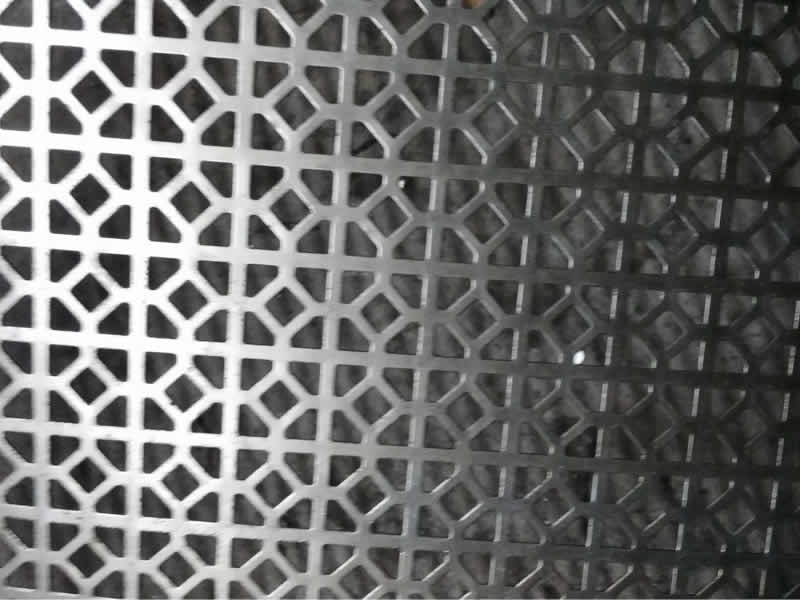
Materials
Perforated metal is crafted from several different materials, each chosen for specific properties and applications.
- Carbon Steel: Commonly used for its strength and affordability, ideal for industrial and structural applications. Available in thicknesses from 0.4mm to 6mm.
- Stainless Steel (Grades 302, 304, 304L, 316, 316L): Offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability, used in environments prone to corrosion. Sheet thicknesses range from 0.5mm to 6mm.
- Aluminum: Known for being lightweight and corrosion-resistant, used primarily in architectural and decorative projects. Thicknesses typically vary from 0.5mm to 4mm.
- Copper and Brass: Valued for their aesthetic qualities and antimicrobial properties, these metals are often used in decorative applications. Available in thicknesses from 0.5mm to 4mm.
- Galvanized Steel (Pre-galvanized, Hot or Cold Galvanized): Provides enhanced corrosion resistance, suitable for outdoor use. Thicknesses for these materials range from 0.5mm to 3mm.
Surface Treatments
Perforated metal undergoes various surface treatments to enhance its durability, appearance, and functionality.
- Electro Galvanized: Applies a thin zinc coating through an electrochemical process, offering mild corrosion resistance for indoor use. Coating thickness is typically between 5 to 25 microns.
- Hot-Dipped Galvanized: Immerses the metal in molten zinc for a thicker coating, providing strong corrosion resistance suitable for outdoor environments. Zinc layers range from 45 to 100 microns.
- PVC Coated: Covers the metal with a layer of PVC to enhance corrosion resistance and provide color options. This coating is about 100 to 400 microns thick, adding smoothness and safety.
- Powder Coating: A dry powder is applied and then cured under heat to create a hard finish in various colors, ideal for both protection and aesthetics. Typical thickness ranges from 60 to 120 microns.
- Oxidation Treatment (Anodizing): Used primarily for aluminum, enhancing its corrosion and wear resistance. Oxide layer thickness is generally around 5 to 25 microns.
Standard Sizes
Perforated metal is available in several common sheet sizes, catering to a wide range of applications:
- 1000mm × 2000mm: Ideal for detailed architectural and decorative uses due to its compact size.
- 1220mm × 2440mm: Aligns with standard 4×8 feet construction materials, suitable for seamless integration in building projects.
- 1500mm x 3000mm: Perfect for large-scale applications like industrial cladding and architectural partitions due to its extensive surface area.
Hole Diameter
Perforated metal is offered with various hole diameters to suit a range of applications, from fine filtration to architectural design:
- 0.5mm to 3mm: Ideal for fine filtration and detailed aesthetic applications, these small holes are perfect for HVAC systems, automotive grilles, and intricate decorative panels.
- 4mm to 10mm: Commonly used for architectural elements such as building facades and interior design features, providing a good balance between openness and structural strength.
- 11mm to 50mm: Best for applications requiring significant airflow and light penetration, such as sound barriers, large screens, and safety guards in industrial settings.
Advantages
Perforated metal stands out due to its unique properties and versatile applications, offering significant advantages across various fields:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Despite the removal of material through perforation, perforated metal retains a high strength-to-weight ratio. This makes it suitable for structural applications where robustness is needed without the burden of excessive weight, enhancing ease of installation and support structures.
- Economical Material Consumption: The perforation process is designed to maximize material usage efficiently, significantly reducing waste compared to other manufacturing processes that remove larger sections of material. This efficiency not only reduces costs but also aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Superior Air and Light Distribution: Perforated metal optimally balances air flow and light diffusion, which can contribute to more sustainable building designs by reducing the need for artificial ventilation and lighting systems, thereby decreasing energy consumption.
- Effective Sound Management: The specific patterns and sizes of the holes in perforated metal can be engineered to disrupt sound waves, effectively reducing noise levels and enhancing acoustic performance in settings such as theaters, conference rooms, and public spaces.
- Decorative and Functional Design Flexibility: With the ability to produce perforations in a wide array of patterns and sizes, from 0.2 mm to 100 mm in diameter, perforated metal offers extensive design versatility. This makes it highly sought after for architectural applications where both aesthetics and functional performance are critical.
- Flexible Size Options: Perforated metal can be customized to exact specifications, with common sheet sizes ranging from 1000mm x 2000mm up to 2000mm x 6000mm. This adaptability in sizing allows it to meet specific needs in projects, minimizing waste and optimizing coverage.



